
The Securities and Exchange Board of India was established on April 12, 1992, by the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
SEBI is managed by six members – one chairman (nominated by Central Government), two members (officers of central ministries), one member (from RBI), and the remaining two members appointed by the Central Government.
The Preamble of the Securities and Exchange Board of India describes the essential functions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India as”…to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of, and to regulate the securities market and for matters connected in addition to that or incidental to it.”
The Securities and Exchange Board of India was established on April 12, 1992, by the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
These Guidelines have been issued by the Securities and Exchange Board of India under Section 11 of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act,1992. (a) These Guidelines may be called the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Disclosure and Investor Protection) Guidelines, 2000. (b) These Guidelines shall come into force from the date specified by the Board.
To understand how SEBI works.
The overall objectives of SEBI are to protect the interest of investors and to promote the development of stock exchange and to regulate the activities of the stock market. The objectives of SEBI are:
Research Methodology refers to the search of knowledge .one can also define research methodology as a scientific and systematic search for required information on a specific topic. The word research methodology comes from the word “advanced learner’s dictionary meaning of research as a careful investigation or inquiry primarily through analysis for new facts in my branch of knowledge; for example, some author has to define research methodology as a systematized effort to gain further understanding
In dealing with the real-life problem, it is often found that data at hand are inadequate, and hence, it becomes necessary to collect data that is appropriate. There are several ways of managing the relevant data which differ considerably in the context of money costs, time and other resources at the disposal of the researcher
A rigid procedure was followed, and we were seeking answers to many pre-conceived questions through personal interviews.
Information to find out the investment potential and goal was found out through surveys.
Information was also taken through telephone calls.
The secondary sources of data are used. (Internet, magazine, books, journals)
Initially, SEBI was a nonstatutory body without any statutory power. However, in 1995, the SEBI was given additional legislative authority by the Government of India through an amendment to the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992. In April 1988, the SEBI was constituted as the regulator of capital markets in India under a resolution of the Government of India.
The SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of the following:
The SEBI performs functions to meet its objectives. To achieve three goals, SEBI has three essential features. These are:

These functions are performed by SEBI to protect the interest of the investor and provide the safety of the investment.
As protective functions, SEBI performs the following features:
These functions are performed by the SEBI to promote and develop activities in the stock exchange and increase the business in the stock exchange. Under developmental categories, the following services are performed by SEBI:
These functions are performed by SEBI to regulate the business in the stock exchange. To monitor the activities of the stock exchange, the following services are implemented:
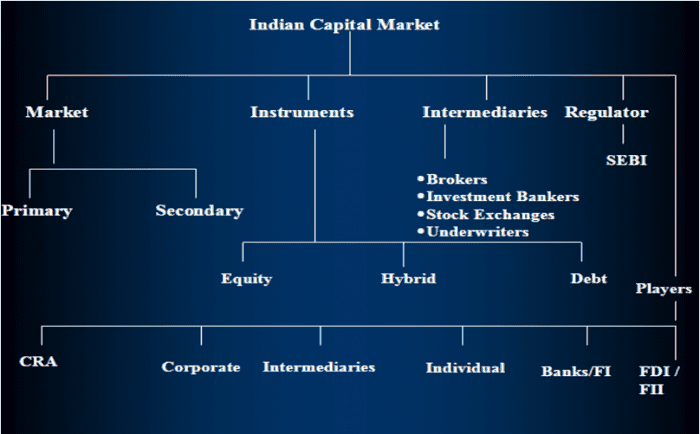
The Organisational Structure of SEBI:
Objectives of the two Committees are:
These committees can only advise SEBI, but they cannot force SEBI to take action on their advice.
With the growth in the dealings of stock markets, a lot of malpractices also started in stock markets such as price rigging, ‘unofficial premium on a new issue, and delay in delivery of shares, violation of rules and regulations of the stock exchange and listing requirements. Due to these malpractices, the customers started losing confidence and faith in the stock exchange. So the government of India decided to set up an agency or regulatory body known as the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
SEBI was set up with the primary purpose of keeping a check on malpractices and protect the interest of investors. It was set up to meet the needs of three groups.
For issuers, it provides a marketplace in which they can raise finance reasonably and efficiently.
For investors, it provides protection and supply of accurate and correct information.
For intermediaries it provides a competitive professional market.
SEBI has three functions rolled into one body: quasi-legislative, quasi-judicial, and quasi-executive. It drafts regulations in its legislative capacity, it conducts an investigation and enforcement action in its executive function, and it passes rulings and orders in its judicial position. Though this makes it very powerful, there is an appeals process to create accountability. There is a Securities Appellate Tribunal, which is a three-member tribunal and is presently headed by a former Chief Justice of a High court -Mr. Justice N.K.Sodhi. A second appeal lies directly to the Supreme Court.SEBI has enjoyed success as a regulator by pushing systemic reforms aggressively and successively. SEBI has been active in setting up the regulations as required under the law.SEBI has also been instrumental in taking quick and practical steps in light of the global meltdown and the Satyam fiasco. It had increased the extent and quantity of disclosures to be made by Indian corporate promoters. More recently, in light of the global meltdown, it liberalized the takeover code to facilitate investments by removing regulatory structures. In one such move, SEBI has increased the application limit for retail investors to Rs 2 lakh, from Rs 1 lakh at present.
The Capital Market Regulator, SEBI, has carefully developed proper stability mechanisms to keep the Market functioning with stability and sustainability. There are difficulties, but the Capital Market Regulator devises careful working strategies to overcome them. Such plans come in the form of rules, regulations, and innovative market reforms. SEBI has been granted powers by the Law Courts and the Government of India, which helps its machinery to function as expected.
SEBI is very much engaged in the education of investors and the careful training of all Capital Market participants. This is the source of stability and sustainability in the Indian Capital Market. The situation of the Indian Capital Market is evidence of the fact that investors’ interest is well protected. They should have confidence in the market and invest without fear of abnormal or excess losses.
After discussing this topic with my friends, we all believed that SEBI is helping India to achieve great heights. It protects the investors and educates them carefully for Capital market participants.
I believe that SEBI needs to be vested with more powers; among this mention may be made of the following important ones:
My profound gratitude to all the faculty members of the Department, for their timely assistance and encouragement throughout my research work.
I duly acknowledge the encouragement and support of the research scholars in the department, and all my colleagues and friends.
I thank my friends in the stock market and the management of broking firms who helped me with valuable data in time.
It gives me immense pleasure to take the opportunity to all the people who are directly or indirectly involved in the completion of my project based on Functional report of SEBI
With deep reverence, I offer my deepest gratitude _____, without whom this project could not have been fulfilled.
Lastly, I thank Almighty, my parents, family members, friends, and teachers for their constant encouragement and support, without which this project would not be possible.
Name of School/College